#include "filesys/free-map.h"#include <bitmap.h>#include <debug.h>#include "filesys/file.h"#include "filesys/filesys.h"#include "filesys/inode.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| void | free_map_init (void) |
| Initializes the free map. More... | |
| bool | free_map_allocate (size_t cnt, block_sector_t *sectorp) |
| Allocates CNT consecutive sectors from the free map and stores the first into *SECTORP. More... | |
| void | free_map_release (block_sector_t sector, size_t cnt) |
| Makes CNT sectors starting at SECTOR available for use. More... | |
| void | free_map_open (void) |
| Opens the free map file and reads it from disk. More... | |
| void | free_map_close (void) |
| Writes the free map to disk and closes the free map file. More... | |
| void | free_map_create (void) |
| Creates a new free map file on disk and writes the free map to it. More... | |
Variables | |
| static struct file * | free_map_file |
| Free map file. More... | |
| static struct bitmap * | free_map |
| Free map, one bit per sector. More... | |
Function Documentation
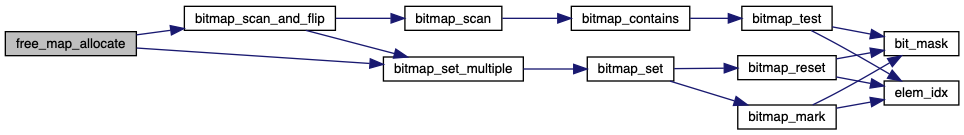
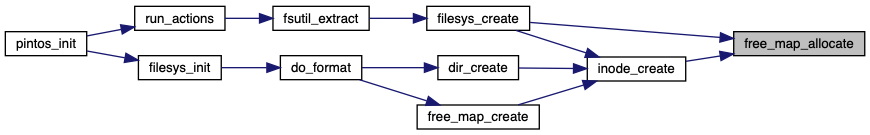
◆ free_map_allocate()
| bool free_map_allocate | ( | size_t | cnt, |
| block_sector_t * | sectorp | ||
| ) |
Allocates CNT consecutive sectors from the free map and stores the first into *SECTORP.
Returns true if successful, false if not enough consecutive sectors were available or if the free_map file could not be written.
Definition at line 28 of file free-map.c.
References BITMAP_ERROR, bitmap_scan_and_flip(), bitmap_set_multiple(), free_map, free_map_file, and NULL.
Referenced by filesys_create(), and inode_create().
◆ free_map_close()
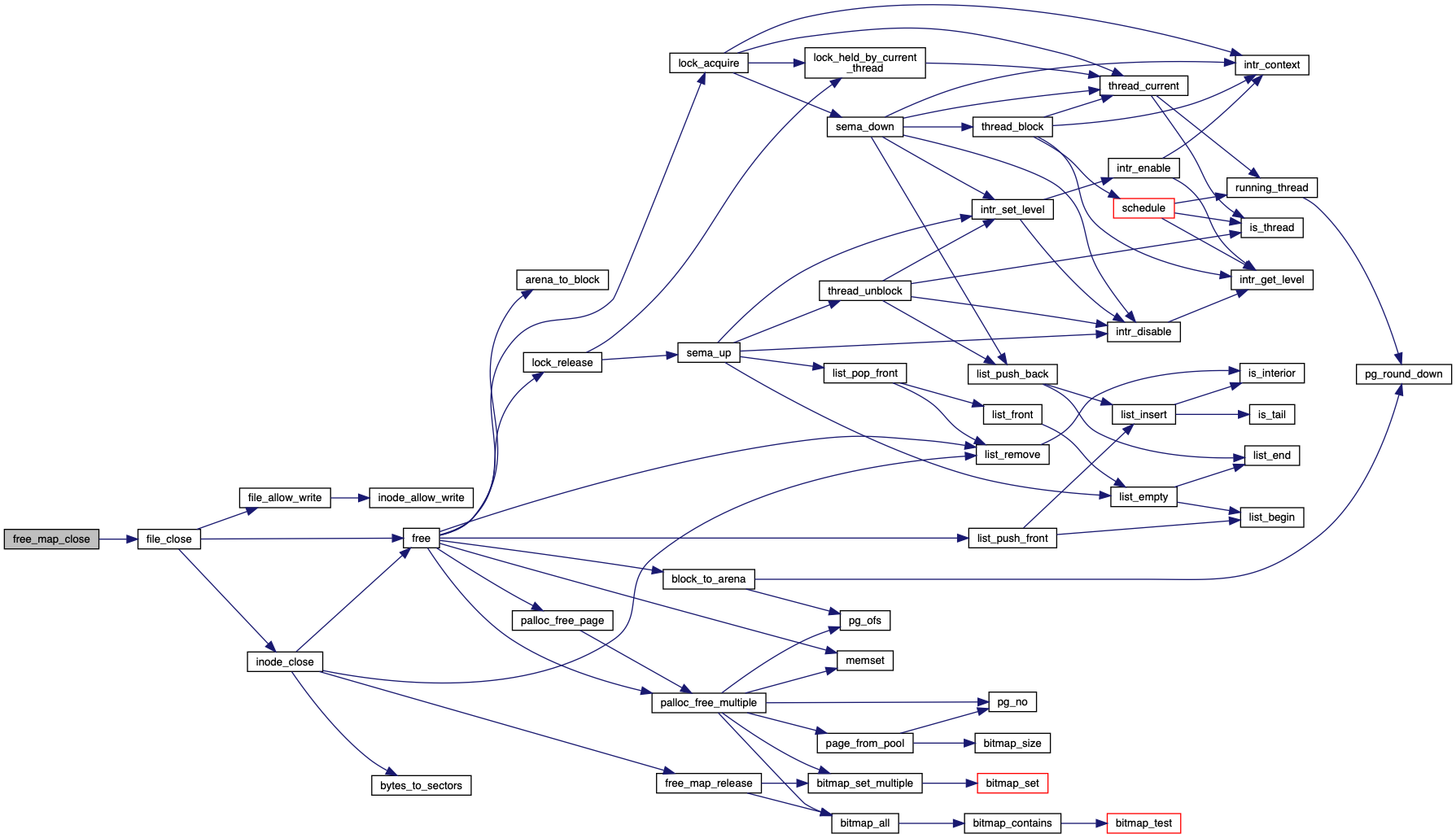
| void free_map_close | ( | void | ) |
Writes the free map to disk and closes the free map file.
Definition at line 65 of file free-map.c.
References file_close(), and free_map_file.
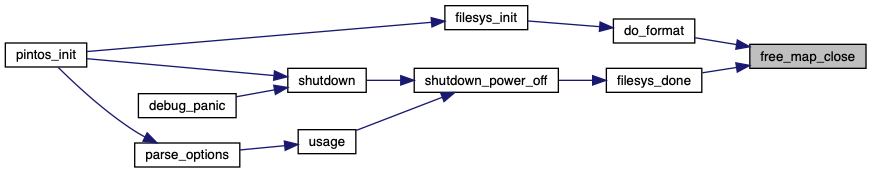
Referenced by do_format(), and filesys_done().
◆ free_map_create()
| void free_map_create | ( | void | ) |
Creates a new free map file on disk and writes the free map to it.
Definition at line 73 of file free-map.c.
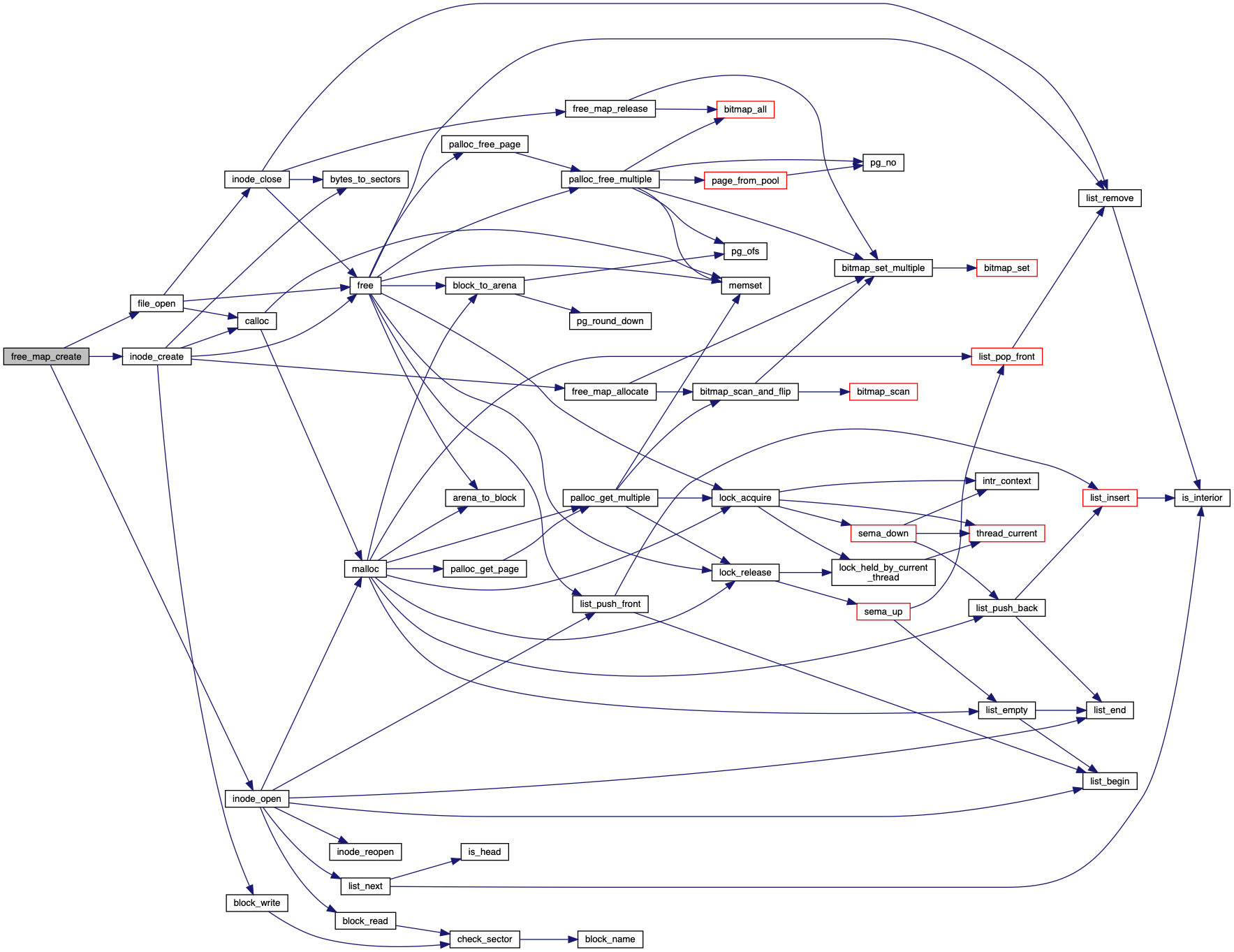
References file_open(), free_map, free_map_file, FREE_MAP_SECTOR, inode_create(), inode_open(), NULL, and PANIC.
Referenced by do_format().

◆ free_map_init()
| void free_map_init | ( | void | ) |
Initializes the free map.
Definition at line 13 of file free-map.c.
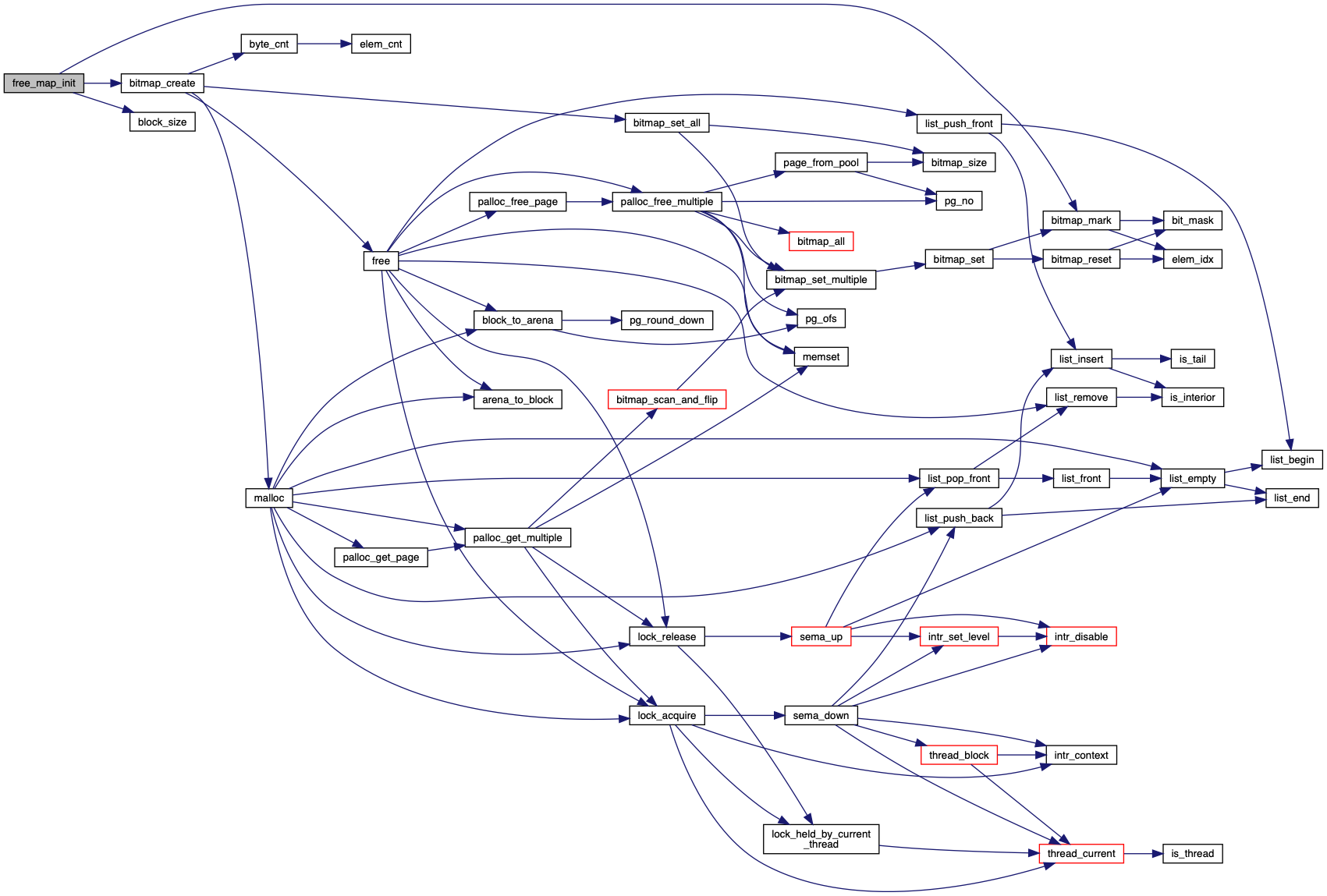
References bitmap_create(), bitmap_mark(), block_size(), free_map, FREE_MAP_SECTOR, fs_device, NULL, PANIC, and ROOT_DIR_SECTOR.
Referenced by filesys_init().

◆ free_map_open()
| void free_map_open | ( | void | ) |
Opens the free map file and reads it from disk.
Definition at line 54 of file free-map.c.
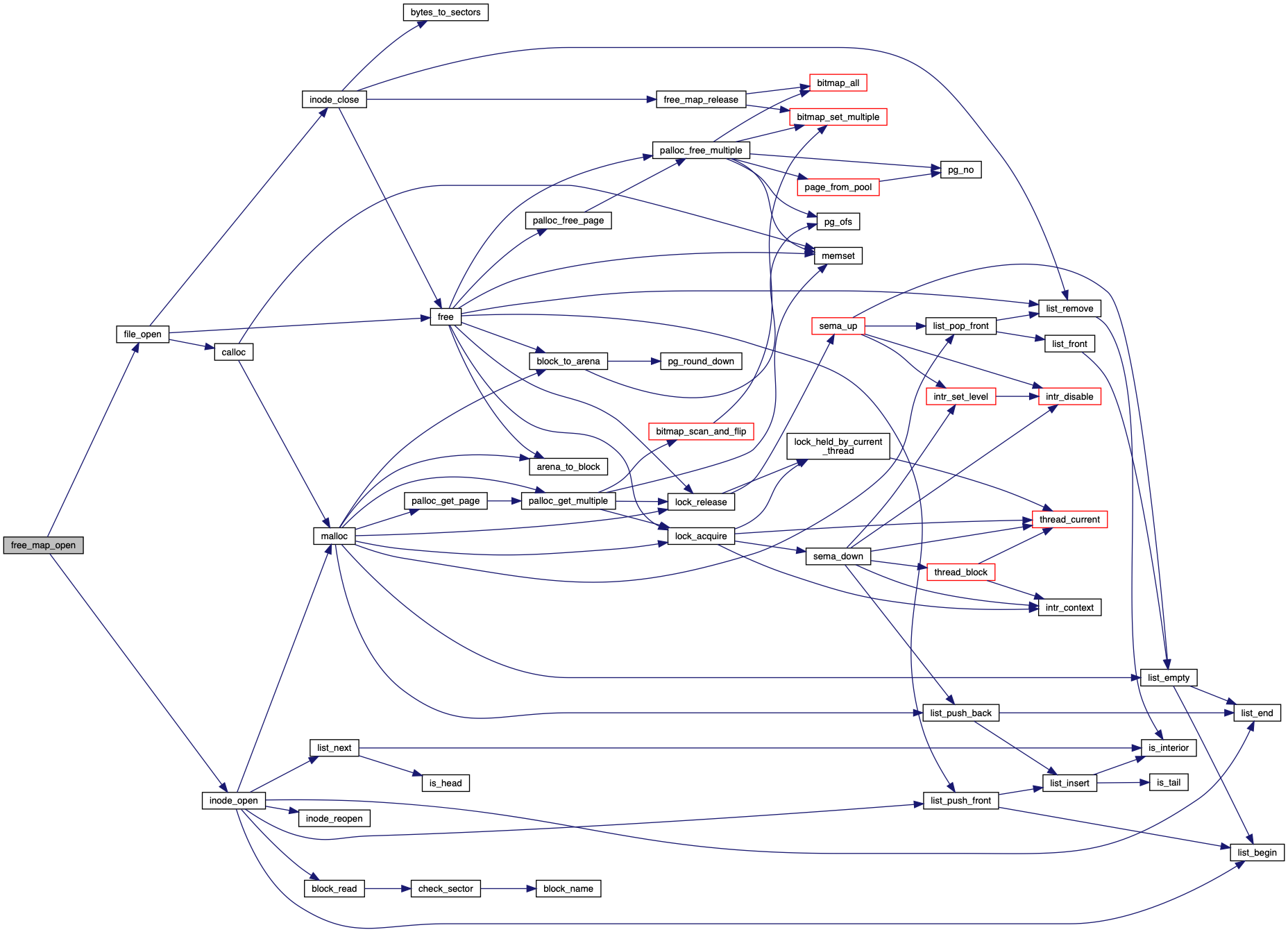
References file_open(), free_map, free_map_file, FREE_MAP_SECTOR, inode_open(), NULL, and PANIC.
Referenced by filesys_init().

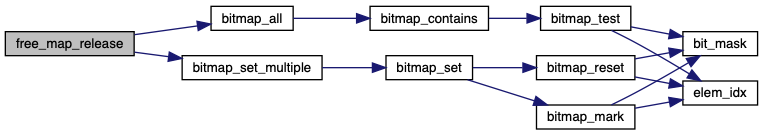
◆ free_map_release()
| void free_map_release | ( | block_sector_t | sector, |
| size_t | cnt | ||
| ) |
Makes CNT sectors starting at SECTOR available for use.
Definition at line 45 of file free-map.c.
References ASSERT, bitmap_all(), bitmap_set_multiple(), free_map, and free_map_file.
Referenced by filesys_create(), and inode_close().
Variable Documentation
◆ free_map
|
static |
Free map, one bit per sector.
Definition at line 9 of file free-map.c.
Referenced by free_map_allocate(), free_map_create(), free_map_init(), free_map_open(), and free_map_release().
◆ free_map_file
|
static |
Free map file.
Definition at line 8 of file free-map.c.
Referenced by free_map_allocate(), free_map_close(), free_map_create(), free_map_open(), and free_map_release().
 1.8.16
1.8.16